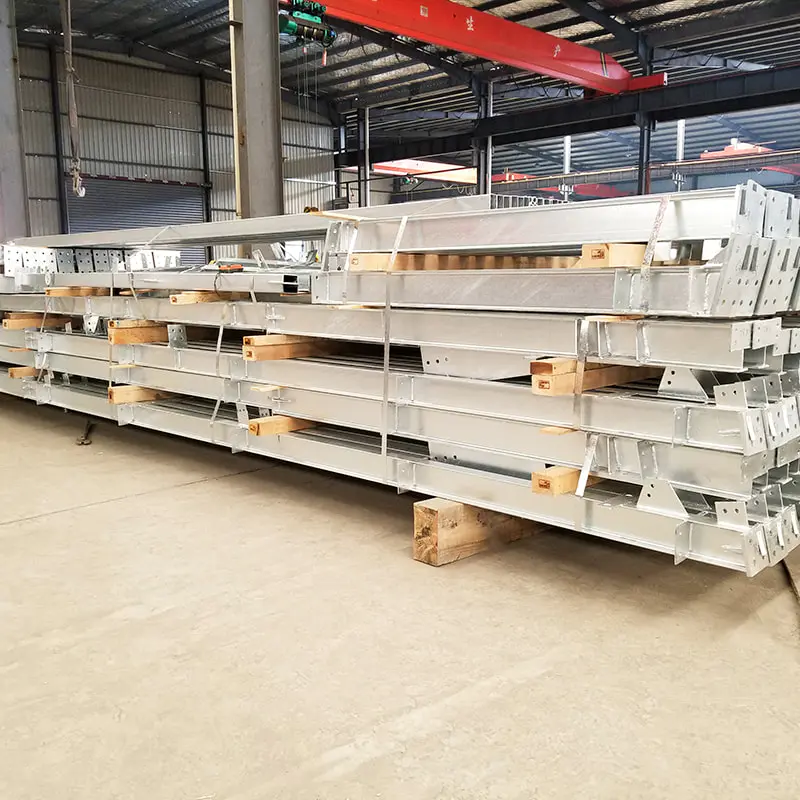
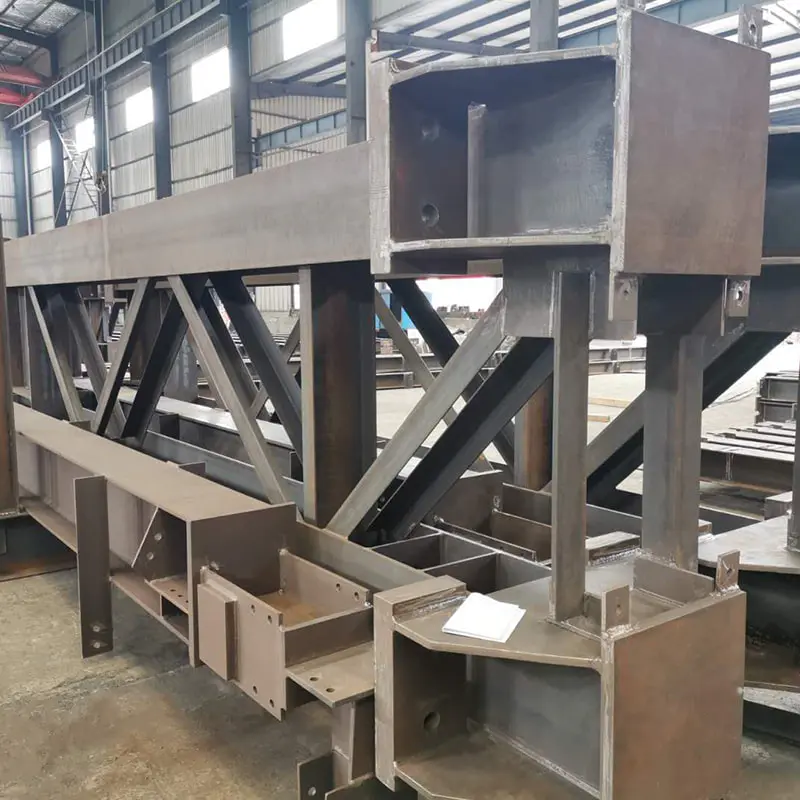
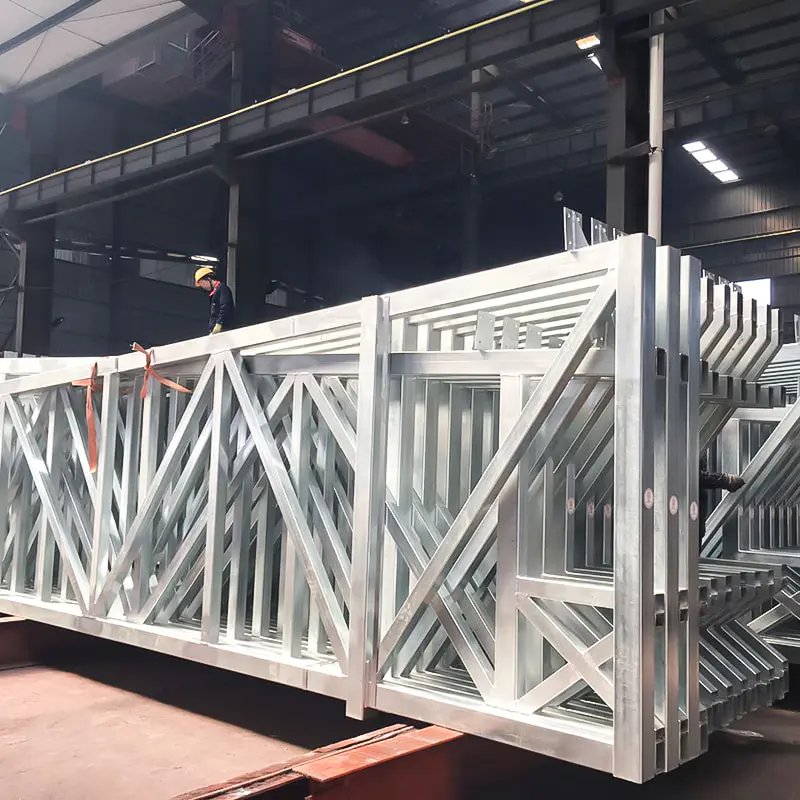
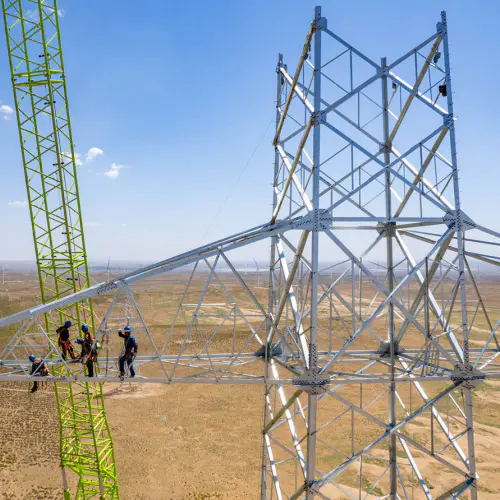
The use of Steel Columns and Beams in warehouses and workshops is foundational to modern industrial construction, offering unmatched strength, durability, and design flexibility. However, their safe implementation hinges on adherence to rigorous safety standards that govern design, fabrication, and installation.
1. International Building Codes (IBC) and Regional Regulations
Globally, the International Building Code (IBC) sets baseline requirements for structural steel systems, including Steel Columns and Beams. The IBC mandates load-bearing calculations, fire resistance ratings, and seismic performance criteria tailored to geographic risks. Regional adaptations, such as the Eurocode 3 in Europe or the AISC 360 Specification in the U.S., provide localized guidelines for material grades, weld quality, and permissible deflection limits.
For warehouses storing heavy machinery or workshops with dynamic loads, compliance with live load and wind load specifications (e.g., ASCE/SEI 7-22) is non-negotiable. These standards ensure Steel Columns and Beams can withstand stressors without compromising structural stability.
2. Material and Fabrication Standards
The quality of Steel Columns and Beams begins with material selection. Standards like ASTM A992 (for rolled steel shapes) and EN 10025 (European structural steel grades) define minimum yield strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Fabrication processes, including welding and bolting, must align with codes such as AWS D1.1 (American Welding Society) to prevent joint failures.
Third-party inspections during manufacturing are often required to verify dimensional accuracy and coating integrity, particularly for fireproofing or rust prevention—a critical factor in humid or chemically intensive environments.
3. Installation and Occupational Safety Protocols
Proper installation of Steel Columns and Beams demands adherence to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines in the U.S. or equivalent bodies elsewhere. These include crane operation safety, fall protection for workers, and temporary bracing during assembly. Post-installation, structures must undergo load testing and alignment checks to confirm they meet design tolerances.
4. Ongoing Maintenance and Inspection
Safety extends beyond construction. Regular inspections, as outlined by organizations like the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), are vital to detect corrosion, fatigue cracks, or accidental impacts. Advanced techniques, such as ultrasonic testing or 3D laser scanning, help identify flaws invisible to the naked eye.
Why Compliance Matters
Ignoring these standards risks catastrophic failures. For example, improper welding or overloaded beams can lead to buckling or collapse, endangering lives and incurring legal liabilities. Conversely, compliant Steel Columns and Beams enhance operational longevity, reduce insurance costs, and align with sustainability goals by minimizing material waste.
The safe use of Steel Columns and Beams in warehouses and workshops is a multifaceted responsibility. By integrating international codes, material excellence, precise installation, and proactive maintenance, stakeholders can ensure these critical components uphold both safety and efficiency for decades. In an era where industrial demands are escalating, adherence to established standards is not just regulatory—it’s a moral imperative.